Trigonometry
| Site: | WelTec Moodle |
| Course: | Learning Services |
| Book: | Trigonometry |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Monday, 29 April 2024, 2:12 AM |
Description
Learn the basics of trigonometry. Trigonometry will help you solve right angled triangles.
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Example 1
- Practice Question 1
- Practice Question 1 Answer
- Practice Question 2
- Practice Question 2 Answer
- Example 2
- Practice Question 3
- Practice Question 3 Answer
- Practice Question 4
- Practice Question 4 Answer
- Example 3
- Practice Question 5
- Practice Question 5 Answer
- Practice Question 6
- Practice Question 6 Answer
Introduction
Trigonometry is a method of calculating the length of the sides of a right angled triangle. The trigonometrical ratios are sine, cosine and tangent. These are shortened to sin, cos and tan.
You can find the sine, cosine or tangent of any angle on your calculator. You will need to know the following formulas:
Sine = Opposite side ÷ Hypotenuse
Cosine = Adjacent side ÷ Hypotenuse
Tangent = Opposite ÷ Adjacent
Use the arrows to click through the pages to view example problems and practice questions, or click the link below to download a printable copy of these activities.
Example 1
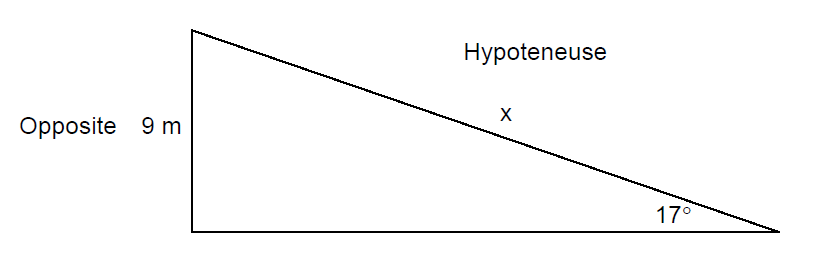
Use trigonometry to find the hypotenuse in the triangle below. You have been given the opposite side and the angle.
Remember:
Sine = Opposite ÷ Hypotenuse
Cosine = Adjacent ÷ Hypotenuse
Tangent = Opposite ÷ Adjacent
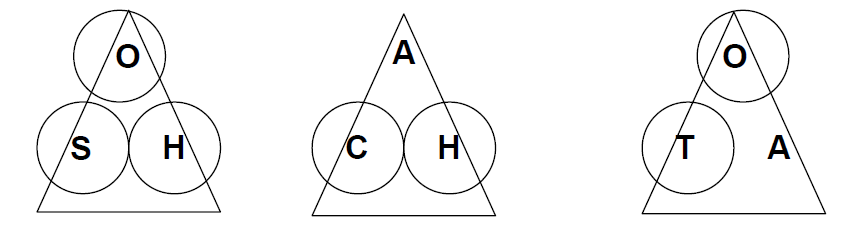
Cover up the information you have, and the information you are trying to find in the working triangles below.
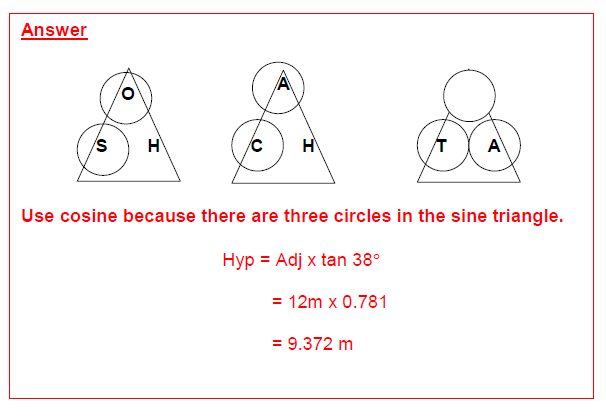
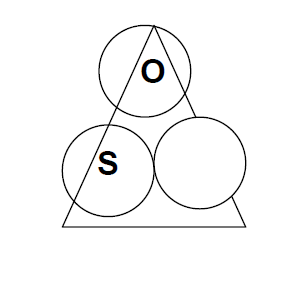
Use sine because there are three circles in the sine triangle.
Now that you have decided to use the sine ratio, you can use this working triangle to work out the hypotenuse.
Cover up the H because you are trying to find the hypotenuse.
This means that you have to divide the opposite by the sine of 17°
Hyp = Opp ÷ sin 17°
= 9m ÷ 0.292
= 30.822m
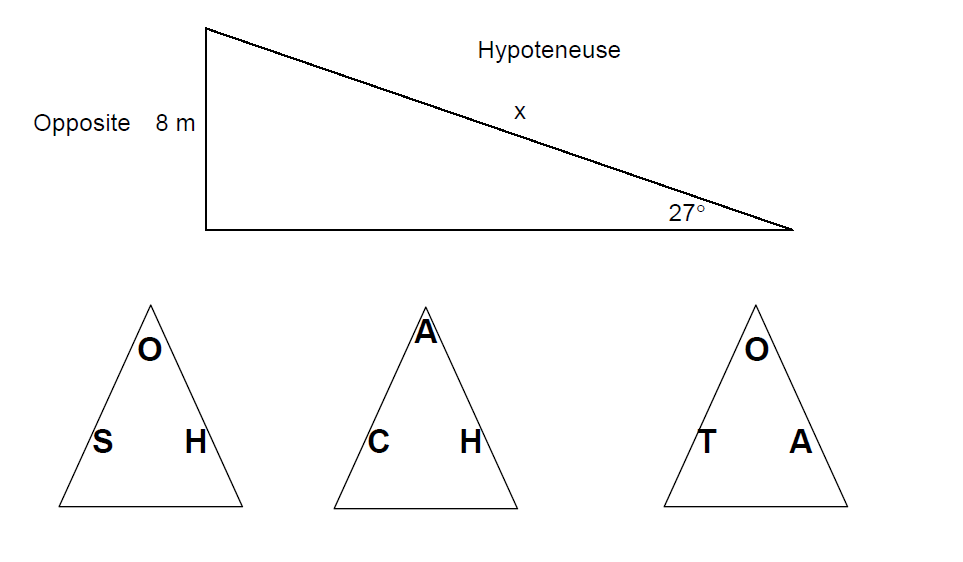
Practice Question 1
Use trigonometry to find the hypotenuse of the triangle below.
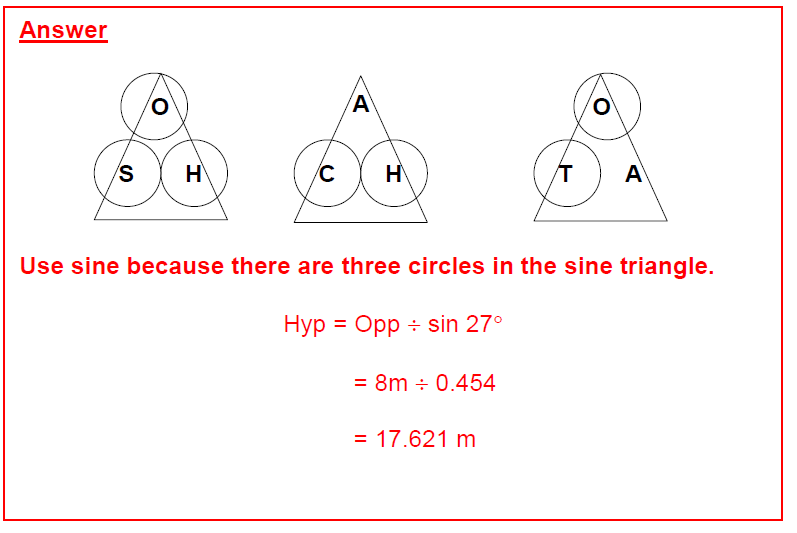
Practice Question 1 Answer
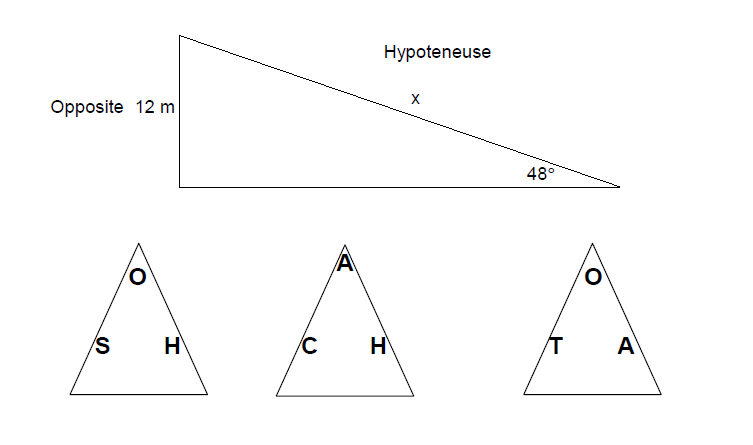
Practice Question 2
Use trigonometry to find the hypotenuse of the triangle below.
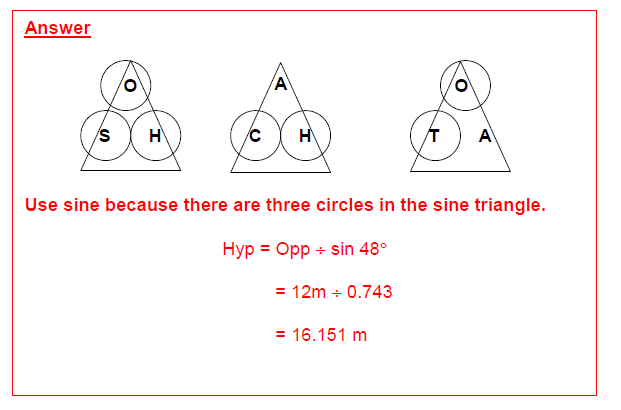
Practice Question 2 Answer
Example 2
Use trigonometry to find the length of the hypotenuse in the triangle below. You have been given the adjacent side and the angle.
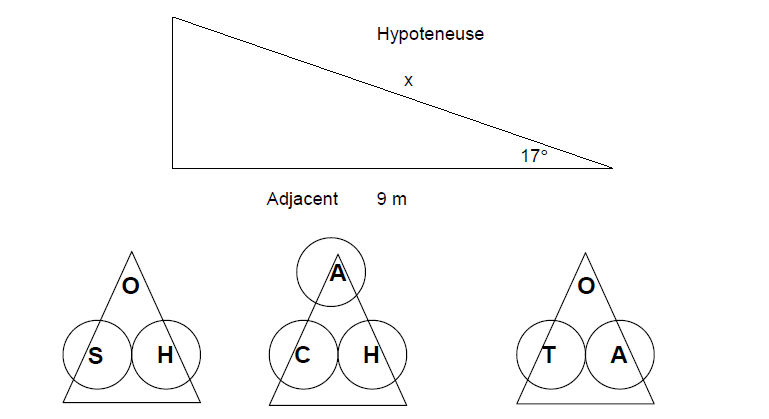
Cover up the information you have, and the information you are trying to find in the working triangles below.
Use cosine because there are three circles in the cosine triangle.
Cover up the H because you are trying to find the hypotenuse.
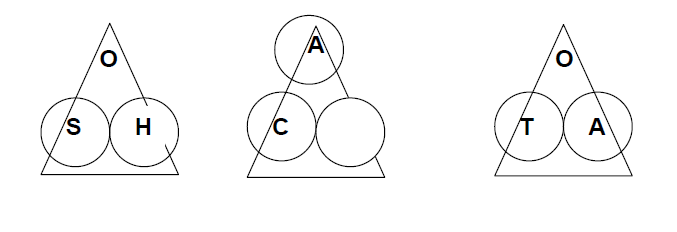
This means that you have to divide the adjacent by the cosine of 17°
Hyp = Adj ÷ cos 17°
= 9m ÷ 0.956
= 9.414m
Practice Question 3
Use trigonometry to find the hypotenuse in the triangle below.
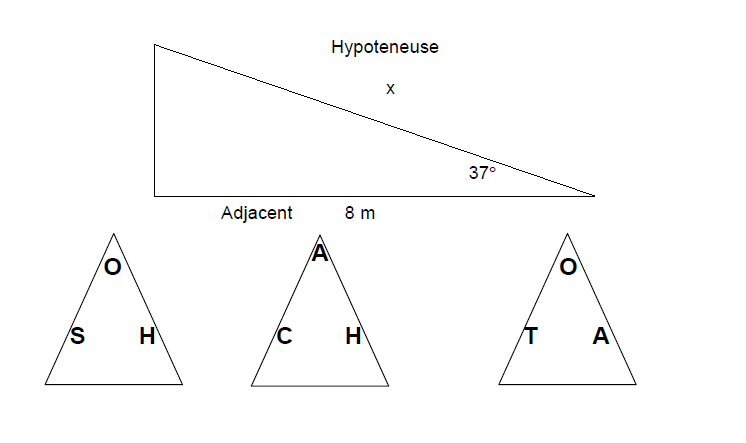
Practice Question 3 Answer
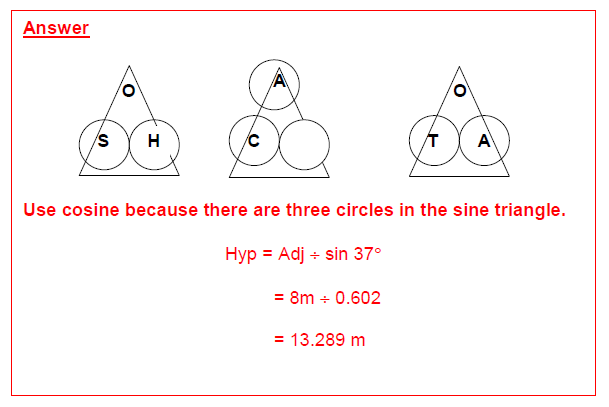
Practice Question 4
Use trigonometry to find the hypotenuse in the triangle below.
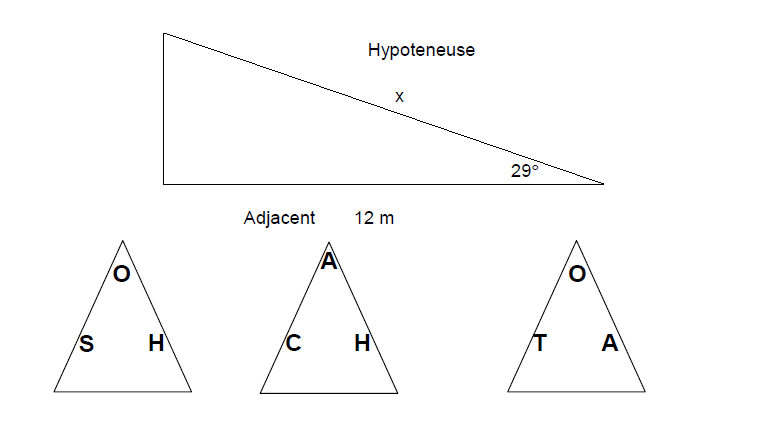
Practice Question 4 Answer
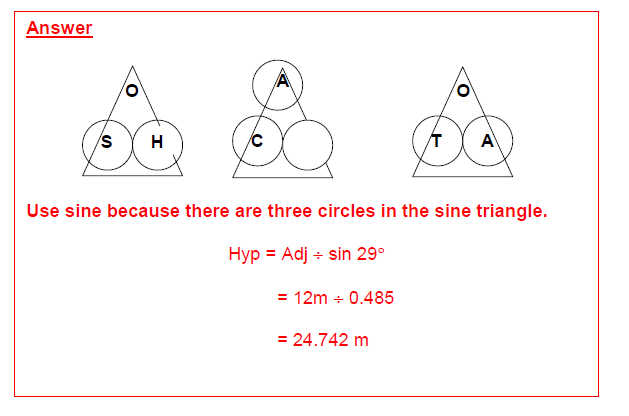
Example 3
Use trigonometry to find the opposite side in the triangle below. You have been given the adjacent side and an angle.
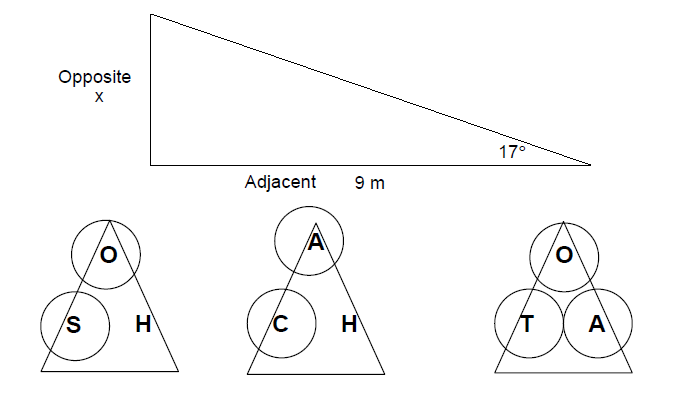
Cover up the information you have, and the information you are trying to find in the working triangles above.
Use tangent because there are 3 circles in the tangent triangle.
Cover up the O because you are trying to find the opposite.
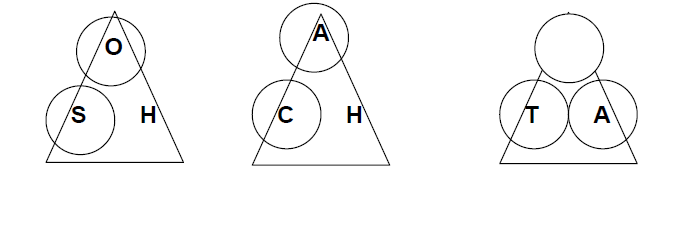
This means that you have to multiply the adjacent by the tangent of 17°
Opp = Adj x tan17°
= 9m x tan17°
= 2.752m
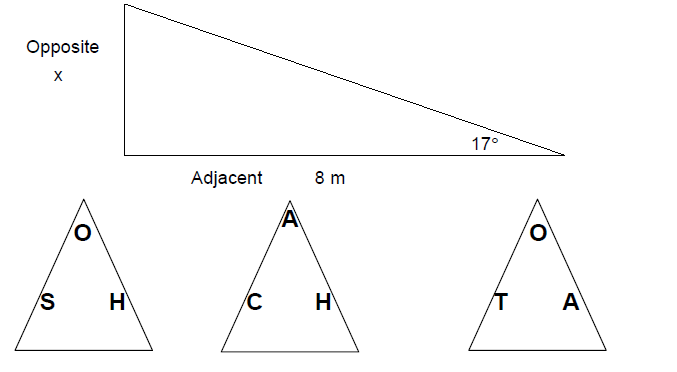
Practice Question 5
Find the opposite side in the triangle below.
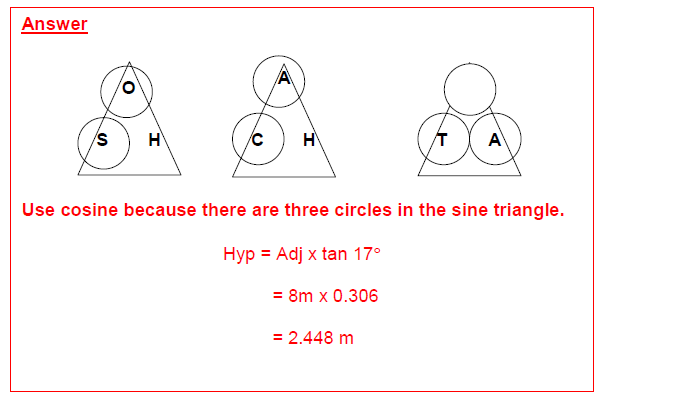
Practice Question 5 Answer
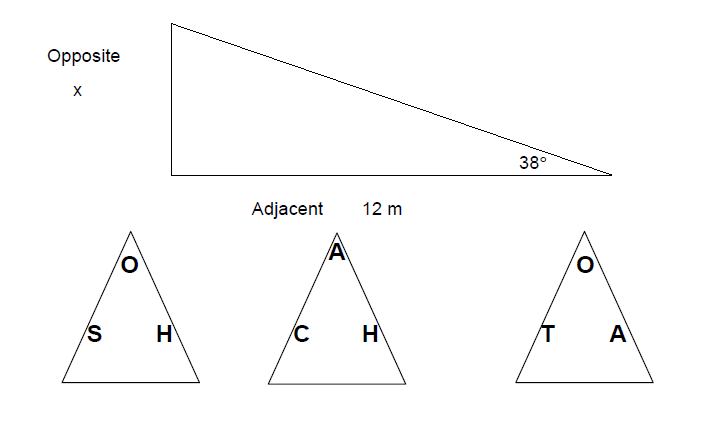
Practice Question 6
Find the opposite side in the triangle below.
Practice Question 6 Answer